International Blue Flag hoisted at 8 beaches across the Country
News: Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change has virtually hoisted the international blue flags in 8 beaches across the country.
Facts:
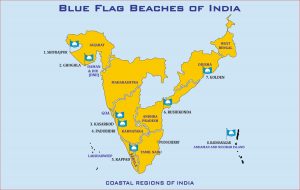
- During October 2020; Eight beaches of India spread across five states and two union territories have been awarded the Blue Flag Certification. These eight beaches are:
- Shivrajpur (Dwarka-Gujarat)
- Ghoghla (Diu)
- Kasarkod and Padubidri (Karnataka)
- Kappad (Kerala)
- Rushikonda (AP)
- Golden (Puri-Odisha) and
- Radhanagar (A&N Islands).
- India has also set up an ambitious target of getting the Blue Certification tag for 100 more beaches in the next 3 years.
Additional Facts:
- Blue flag certification: It is an international recognition conferred on beaches that meet certain criteria of cleanliness and environmental propriety.
- The certification programme is run by the international, non-governmental, non-profit organisation FEE (the Foundation for Environmental Education).
- Criteria: The certification is based on 33 stringent criteria in four major heads (i) Environmental Education and Information (ii) Bathing Water Quality, (iii) Environment Management and Conservation and (iv) Safety and Services in the beaches.
- Headquarters: Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Receiving Blue Flag Certification is an indication of high environmental and quality standards and certified beaches are considered the world’s cleanest beaches. Certification will promote tourism to the listed beaches in India.
- India is now the first country in the “Asia-Pacific” region which has now in the league of 50 “BLUE FLAG” countries that too in just about 2 years’ time.
India’s initiative to get Blue Flags: BEAMS (Beach Environment & Aesthetics Management Services) ZM (Integrated Coastal Zone Management) project in order to undertake the sustainable development of coastal regions and to achieve the goal of having Blue Flags for 100 beaches in India.
- Objectives: The objectives of BEAMS program is to:
- Abate pollution in coastal waters,
- Promote sustainable development of beach facilities,
- Protect & conserve coastal ecosystems & natural resources,
- Strive and maintain high standards of cleanliness,
- Hygiene & safety for beachgoers in accordance with coastal environment & regulations.
1000-yrs Old Monpa Handmade Paper Industry revived
News: Khadi and Village Industries Commission(KVIC) has revived the 1000 year old Monpa Handmade Paper of Arunachal Pradesh by commissioning a Monpa handmade paper making unit in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh. The paper unit will also serve as a training center for the local youths to sustain the tradition.
Facts:
- Monpa Handmade Paper: It is an heritage hand paper artform of Arunachal Pradesh. This handmade paper is also called as Mon Shugu in the local dialect and is integral to the vibrant culture of the local tribes in Tawang.
- Origin: The art of making originated among the Monpas over 1000 years ago. Gradually this art became an integral part of local custom and culture of Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Why did it decline? Monpas paper used to be sold to countries like Tibet, Bhutan ,Thailand and Japan as no paper making industry existed in these countries at that time.
- However, the local industry gradually began declining and the indigenous handmade paper was taken over by inferior Chinese paper.
- How will it be made now? The fine-textured Monpa handmade paper will be made from the bark of a local tree called Shugu Sheng, which has medicinal values too. Hence availability of raw material will not be a problem.
- Significance: The paper has great historic and religious significance as it is the paper used for writing Buddhist scriptures and hymns in monasteries.
India’s First Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine “Pneumosil”
News: Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare has inaugurated India’s first pneumococcal conjugate vaccine(PCV) named “Pneumosil”.
Facts:
- Pneumosil: It has been developed by the Serum Institute of India Private Limited (SIIPL) in collaboration with partners like the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Pneumosil was licensed by the Drugs Controller General (India) in July 2020.
What is Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine(PCV)?
- It is a pneumococcal and a conjugate vaccine used to protect infants, young children and adults against disease caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus).
- Conjugate: It is a type of vaccine that joins a protein to an antigen in order to improve the protection the vaccine provides.
- It contains purified capsular polysaccharide of pneumococcal serotypes conjugated to a carrier protein to improve antibody response.
- The unique feature of the PCV is its composition which is specially tailored to the prevailing serotype prevalence of S Pneumoniae in India and other regions of the world.
What is Pneumococcal disease?
- Pneumococcal disease is the name given to a group of diseases caused by a bacterium called Streptococcus pneumoniae, (also known as pneumococcus).
- Diseases caused by pneumococcus include 1) severe diseases such as pneumonia, meningitis and bacteraemia (presence of bacteria in the blood) and 2) milder diseases such as middle ear infection (otitis media), sinusitis and bronchitis.
- Cases: Pneumococcal disease is a significant contributor to the under-five mortality rate worldwide.Annually India witnesses an estimated 71% of pneumonia deaths and 57% of severe pneumonia cases.Every year, nearly 67,800 children under five years of age die from pneumococcal diseases.
- Vaccine: Hence, recognising its widespread fatality, WHO recommended the inclusion of PCV in routine childhood immunisation programmes in all countries.
IIT-Delhi’s scientist receives UNDP first prize for innovation of plant-based mock egg
News: A team of scientists from IIT Delhi won an innovation contest (Innovate 4 SDG) organised by the United Nation Development Programme (UNDP) Accelerator Lab India for their innovation of a “plant based mock egg”.
Facts:
- Mock Egg: It has been developed from very simple farm based crop proteins, which not only looks and tastes like an egg but is also very close in nutritional profile to poultry eggs.
- Significance: The development of the mock egg meets the protein needs of the diet-specific, health conscious, vegan and vegetarian people and will also help in addressing the longstanding battle for malnutrition and clean protein food for people.
Additional Facts:
- UNDP’s Accelerator Lab: It is an innovative initiative by UNDP, State of Qatar and the Federal Republic of Germany to find 21st century solutions to today’s complex new challenges.
- UNDP Accelerator Lab India: It is a part of a network of 60 global labs covering 78 nations that tests and scales new solutions to global challenges like climate change and inequality.
- Objective: It seeks to address some of the most pressing issues facing India, such as air pollution, sustainable water management and client-resilient livelihoods through innovation.
Explained: The signature of Kahn and other foreign architects on Indian cities
News: A controversy has erupted over a decision by the Indian Institute of Management(IIM), Ahmedabad to bring down 18 dormitories built by legendary American architect Louis Kahn on the old campus and replace them with a new building.In this Context, let us look at the contributions of different architects on Indian Cities,
Facts:
- Antonin Raymond & George Nakashima: Golconde, India’s first reinforced concrete buildings built between 1937 and 1945 in Puducherry was designed and completed by them.
- Otto Königsberger: He was the chief architect and planner of Mysore State between 1939 and 1948.Later, he was commissioned by Tata & Sons to develop the industrial township of Jamshedpur in the early 1940s.He also later designed the master plan for Bhubaneswar(1948) and Faridabad(1949).
- Albert Mayer and Mathew Nowicki: They designed the city of Chandigarh.
- Le Corbusier: He was a Swiss-French architect.He designed many of Chandigarh’s civic buildings from courts to housing.He is often called the “father of modern Indian architecture”.
- Patrick Geddes: He wrote town planning reports from 1915 to 1919, for 18 Indian cities including Bombay and Indore.
- Frank Lloyd Wright: He was an American architect.He never built a structure in India but his influence was unmistakable.His students, Gautam and Gira Sarabhai were the founders of the National Institute of Design, Ahmedabad.
- Buckminster Fuller: He is known for his geodesic domes – large-span structures made of a network of triangles.Gautam Sarabhai inspired by Fuller designed the Calico Dome in 1962 in Ahmedabad, Gujarat at the same site that served as a mill shop.
- Joseph Allen Stein: He was an American architect.He is known for designing important buildings in India most notably in Lodhi Estate in Delhi nicknamed Steinabad after him.He is also famous for being the architect of the scenic Indian Institute of Management Kozhikode’s campus.
- Louis Kahn: He was an American architect.He designed the old campus of IIM Ahmedabad.The plan’s most distinctive features are the numerous arches, and square brick structures with circles carved out in the façade.
PM launches India’s first driverless metro train in Delhi
News: The Prime Minister of India has flagged off the country’s first ‘driverless’ metro in Delhi.
Facts:
- Delhi driverless Metro train: It will be rolled out on the 38-km Line 8 or Magenta Line of the Delhi Metro which has a 390-km-long network spread across the national capital and adjoining cities.
- Significance: After this inauguration, Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) has entered the elite league of 7% of the world’s Metro networks which can operate without drivers.
- How will it benefit the citizens?
- Operational flexibility & efficiency
- Inspection/testing to be done remotely ensuring Higher reliability with no human intervention
- Improved safety and quality of service
- Save Train Operators’ time & effort and improve the quality of his/her job.
What does Driverless Metro Train mean?
- Driverless technology does not mean that there will be no driver – at least that is not going to be the case to begin with. It does mean though that slowly the role of the driver will get more and more limited as the technology and its systems expand.
- Grades of Automation: The driverless train technology has set standards for automation known as Grades of Automation(GoA).
- In GoA 1, the train is run by one driver.
- In GoA 2 and GoA 3, the driver only needs to operate doors and take over if there is an emergency.Trains start and stop in automated mode in GoA2 & 3.
- The last level is GoA 4, where trains run on complete unattended mode.
Four States begin dry run for roll-out of vaccine
News: The dry run to test preparedness for the nationwide roll-out of a COVID-19 vaccine kicked off in four States — Assam, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat and Punjab.
Facts:
- What is a dry run? A dry run is aimed at testing the planned operations and the laid out mechanisms for Covid-19 vaccination in the state. It will provide insights into any gaps or bottlenecks so that those could be addressed before the commencement of the actual drive.
- Will actual vaccines be used in the dry run? No, the dry run process will include all the steps except for the vaccination part.
- What will the dry run include? The mock drill will include:
- Registration of the beneficiary on Co-Win, the platform that will facilitate vaccination
- Testing the allocation of vaccination site
- Process to be followed at the site of vaccination
- Testing cold storage and transportation arrangements.
Additional Facts:
- CoWIN: It is a digitalised platform launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) to help agencies keep a track of Covid-19 vaccination programme and allow Indian citizens to apply for a Covid-19 vaccine shot.
For Further Read on CoWIN: https://blog.forumias.com/cowin-grand-challenge-cowin-platform-and-cowin-app/