BPRD releases data on police Organisations
News: Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) has released data on police organisations.
Facts:
- The data shows different aspects of policing in the country like woman police, police expenditure, constabulary ratio, transport facilities, communication facilities, representation of various castes and police training centres.
Key Takeaways:
- Police Population Ratio: According to report, Population Per Police Person is 511.81, that is one policeman for every 511.81 persons and 3.9 policemen for each VIP. Bihar had the worst ratio with one policeman for 867.57 persons.
- VIP Protection: As many as 66,043 policemen were deployed to protect 19,467 Ministers, Members of Parliament, judges, bureaucrats and other personalities in 2019 compared to 63,061 policemen for similar duty in 2018.
- The highest number of persons who received police protection in 2019 were in West Bengal — 3,142 followed by Punjab (2,594), Bihar (2,347), Haryana (1,355) and Jharkhand (1,351).
- The Backward Classes, Dalits and Tribals constitute almost 67% of India’s population but their representation in police forces in the country is only at 51%.
- Scheduled Tribes form 8.6% of the population and have 12% representation in the police forces, placing them at a comparatively better position.
- Dalits represent 14% of all positions in police forces across the country. According to Census 2011, Dalits make up 16.6% of India’s population.
- Other Backward Classes(OBCs) fare the worst on the representation front as, despite their 41% share in the population, they constitute only 25% of the police forces.
- Women continue to be represented poorly.It is reflected in the women population per woman police ratio which stands at 3,026 nationally
- However, their situation has improved considerably over the past five years. Since 2014, when the actual strength of women in police forces stood at around 1.11 lakh, their representation has almost doubled to 2.15 lakh.
Additional Facts:
- BPR&D: It was established in 1970 with the objective of modernisation of police forces. It functions under the aegis of Union Home Ministry
- BPR&D replaced Police Research and Advisory Council formed in 1966.
- Purpose: It is a nodal national police organisation to study, research and develop on subjects and issues related to policing.
- In 2008, the Government further decided to create the National Police Mission (NPM) under the administrative control of BPR&D
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
Cabinet gives approval for Akash missile export
News: The Union Cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister has approved the export of the Akash Missile system. It also approved the high-level committee formed to expedite clearance of such exports.
Facts:
- Akash Missile: It is an indigenously developed short range Surface-to-air missile with multi-target engagement capability.
- Developed by: The missile has been developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The Missile has been inducted and is operational with the Indian Air Force(IAF) as well as the Indian Army(IA).
- Key Features:
- The missile has a strike range of 25 km.It can reach an altitude of 18 km and can be fired from both tracked and wheeled platforms.
- It has a large operational envelope from a low altitude of 30 metres to a maximum of up to 20 km.
- The system can simultaneously engage multiple targets in Group Mode or Autonomous Mode.
- It has built-in Electronic Counter-CounterMeasures(ECCM) features.The entire weapon system has been configured on mobile platforms.
Additional Facts:
- In August 2020, the Defence Ministry has issued a draft ‘Defence Production & Export Promotion Policy (DPEPP) 2020’ for public feedback with the aim to achieve a manufacturing turnover of $25 bn or ₹1,75,000 crore, including exports of $5 bn in aerospace and defence goods and services by 2025.
Government launches Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomic Consortia(INSACOG) Group
News: Government of India has launched the Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomic Consortia Group(INSACOG).
Facts:
- INSACOG: It has been established to monitor the genomic variations in the SARS-CoV-2 on a regular basis through a multi-laboratory network.
- Composition: It comprises 10 labs (NIBMG Kolkata, ILS Bhubaneswar, NIV Pune, CCS Pune, CCMB Hyderabad, CDFD Hyderabad, InSTEM Bengaluru, NIMHANS Bengaluru, IGIB Delhi and NCDC Delhi).
- Coordinated by: The group is coordinated by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) along with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare(MoH&FW), ICMR and CSIR.
- Nodal Unit for Maintaining Database: National Centre for Disease Control(NCDC) will be the nodal unit for maintaining a database of all samples of the new variants of public health significance. The data will be epidemiologically analysed, interpreted and shared with states for investigation, contact tracing and planning response strategies.
- Other key Functions of the INSACOG:
- It will establish sentinel surveillance for early detection of genomic variants with public health implications and to determine genomic variants in unusual events or trends such as super-spreader events.
- Knowledge generated through this vital research consortium will also assist in developing diagnostics and potential therapeutics and vaccines in the future.
- The group will also closely work with NCDC on activities like SOPs, data annotation, data analysis, data release among others.
India bore maximum brunt of extreme weather events in 2020: Report
News: An International Report titled “Counting the cost 2020: A year of climate breakdown” has been released by Christian aid, a relief and humanitarian agency based in London.
Facts:
- The report listed 15 most destructive climate disasters of 2020 that cumulatively had an expenditure tag of around $150 billion calculated only on insured losses.
Key Takeaways from the report:
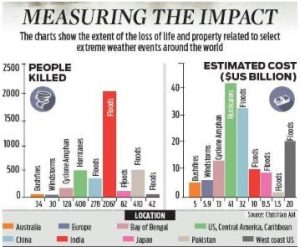
Source: New Indian Express
- Cyclone Amphan which affected countries in the Bay of Bengal and caused maximum damage within coastal districts of West Bengal of India displaced 4.9 million people accounting for the biggest displacement due to an extreme weather event anywhere in the world in 2020.
- Economic Impact: The economic impact of the Cyclone Amphan was fourth in global climate related disaster list following the United States and Caribbean hurricanes, China floods and the United States fires on the west coast.
- Floods in India: The floods in India were the fifth most expensive extreme weather event in the world costing the country $10 billion.
- More importantly, as many as 2,067 lives were lost during the June-October floods, the highest number of fatalities due to climate change-induced weather events this year.
Maiden Flight Trial of Sahayak-NG, Air Droppable Container
News: Defence Research and Development Organisation(DRDO) along with Indian Navy has conducted the successful maiden test trial of ‘SAHAYAK-NG’.
Facts:
- Sahayak-NG: It is India’s first indigenously designed and developed Air Dropped Container from IL 38SD aircraft (Indian Navy) off the coast of Goa.
- Developed by: It has been developed by two DRDO laboratories i.e. NSTL, Visakhapatnam and ADRDE, Agra along with industry partner M/s Avantel for GPS integration.
- Key Features:
- The container can enhance Indian Navy’s operational logistics capabilities and provide critical engineering stores to ships which are deployed more than 2000 km from the coast.
- It also reduces the requirement of ships to come close to the coast to collect spares and stores.
- The GPS aided container also has the capability to carry a payload that weighs up to 50 kg and can be dropped from heavy aircraft.
British lawmakers approve post-Brexit trade deal with EU
News: Britain’s House of Commons has voted resoundingly to approve a trade deal with the European Union paving the way for an orderly break with the European Union(EU).
Facts:
Key Features of the Deal:
The new trade deal:
- Enables the UK to continue selling goods to the EU market – the UK’s biggest trade partner – without tariffs or quotas
- Includes binding enforcement and dispute settlement mechanisms to address any unfair competition – what the EU calls “level playing field” rules
- Ensures continued smooth transport links between the UK and EU, including safeguards on passenger rights
- Means new paperwork and other barriers for UK businesses in Europe, including financial services, which employs more than a million people in the UK
- Transfers 25% of EU boats’ fishing rights in British waters to the UK fleet, over a five-and-a-half year transition period
- Reduces UK access to EU programmes in various fields, including policing and education.
For Further Read on EU-UK Brexit Deal: https://blog.forumias.com/u-k-eu-reach-post-brexit-trade-deal/
Cabinet approves 3 infra projects
News: Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs(CCEA) has approved three key infrastructure proposals.
Facts:
What are the three key infrastructure projects approved? The three projects proposed by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade(DPIIT) are:
- Krishnapatnam Industrial Area in Andhra Pradesh
- Tumakuru (Tumkur) Industrial Area in Karnataka and
- Multi-modal logistics hub (MMLH) and multi-modal transport hub (MMTH) at Greater Noida in Uttar Pradesh.
Additional Facts:
- Industrial Corridor Programme: The objective of the Programme is the creation of greenfield industrial cities with sustainable, ‘plug n play’, ICT enabled utilities to facilitate the manufacturing investments into the country.
- Krishnapatnam Industrial Area and Tumkur Industrial Area are part of Chennai Bengaluru Industrial Corridor(CBIC) project.
- These corridors will help in attracting investments into manufacturing and positioning India as a strong player in the Global Value Chain.
- Multi Modal Logistics Hub(MMLH) & Multi Modal Transport Hub (MMTH): The logistics hub at Greater Noida, UP will be developed as a world-class facility that will provide efficient storage/transitioning of goods to/from the Dedicated Freight Corridors(DFC) and offer a one-stop destination to freight companies and customers.
- The facility will not only provide standard container handling activities but also provide various value-added services to reduce logistics cost with improved efficiency of operations.
Current account surplus moderates to $15.5 bn in Q2
News: The current account surplus moderated to $15.5 billion (2.4% of GDP) in the quarter ended September of 2020-21 from $19.2 billion (3.8% of GDP) in the first quarter this fiscal.The current account saw a deficit of $7.6 billion(1.1%) in the year-ago quarter.
Facts:
- Why has current account surplus narrowed? The narrowing of the current account surplus in Q2 of FY21 was on account of a rise in the merchandise trade deficit to $14.8 billion from $10.8 billion in the preceding quarter.
Current Account:
- What is the Current Account? Current account maintains a record of the country’s transactions with other nations, in terms of trade of goods and services, net earnings on overseas investments and net transfer of payments over a period of time, such as remittances.
- This account goes into a deficit when money sent outward exceeds that coming inward.
- What does Current account constitute? The current account constitutes net income, interest and dividends and transfers such as foreign aid, remittances, donations among others. It is measured as a percentage of GDP.
Current Account = Trade gap + Net current transfers + Net income. abroad
- Why does Current account matter? Current account balance measures the external strength or weakness of an economy.
- A current account surplus implies the country is a net lender to the rest of the world, while a deficit indicates it is a net borrower.
- A country with rising Current Account Deficit(CAD) shows that it has become uncompetitive, and investors are not willing to invest there. They may withdraw their investments.