Arunachal records best sex ratio, Manipur the worst
News: Registrar General of India has released a report titled “vital statistics of India based on the Civil Registration System”.
Facts:
- Civil Registration System(CRS): It is the unified process of continuous, permanent, compulsory and universal recording of the vital events (births, deaths, stillbirths) and characteristics thereof.
Key Takeaways:
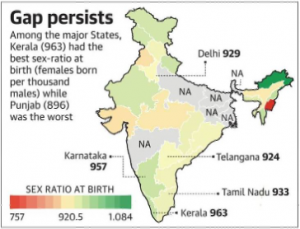
- Best Sex Ratio: Arunachal Pradesh recorded 1,084 females born per thousand males followed by Nagaland (965) Mizoram (964), Kerala (963) and Karnataka (957).
- Worst Sex Ratio: The worst sex ratio was reported in Manipur (757), Lakshadweep (839) and Daman & Diu (877), Punjab (896) and Gujarat (896).
- Registered Births: The number of registered births has increased to 2.33 crore in 2018 from 2.21 crore registered births in 2017.
Additional Facts:
- Sex ratio at birth: It is ratio of number of females born per thousand males.
Explained: What is a Technical Recession?
News: In its latest monthly bulletin, the Reserve Bank of India has said that India has entered a “technical recession” in the first half of 2020-21— for the first time in its history.
Facts:
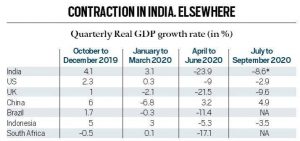
- What is the Technical recession? It is a term used to describe two consecutive quarters of decline in output.In the case of a nation’s economy, the term usually refers to back-to-back contractions in real GDP.
- When does Technical Recession occur? It is most often caused by a one-off event (in this case, the COVID-19 pandemic and the lockdowns imposed to combat it) and is generally shorter in duration.
- Difference between Technical Recession and Recession: The technical recession is mainly used to capture the trend in GDP but the Recession encompasses an appreciably more broad-based decline in economic activity that covers several economic variables including employment, household and corporate incomes and sales at businesses.
Draft rules under Code on Social Security released
News: Union Ministry of Labour and Employment has notified the draft rules under the Code on Social Security,2020.
Facts:
- Objective: To enable operationalisation of provisions in the Code on Social Security,2020 relating to Employees Provident Fund, Employees’ State Insurance Corporation, Maternity Benefit, Social Security and Cess in respect of Construction Workers, Gig Workers and Platform Workers.
Key Provisions of the Rules:
- Registration of gig and unorganised sector workers will be authenticated with their Aadhaar details, following which a unique registration number will be allotted to them.
- Gig firms will be required to make an annual contribution by June 30th of every year for social security of their workers.
- Workers will have to constantly update their details, including residential address, present job, period of engagement with gig firms etc on a web portal to remain eligible for social security benefits.
- Aadhaar-based registration of building and other construction workers (BOCW) on the specified portal of the Central government and the state government or the State Welfare Board.When a building worker migrates from one state to another, he shall be entitled to get benefits in the state where he is currently working.
- Rate of interest for delayed payment of cess by construction firms to be reduced from 2% to 1% every month.
- Labour assessing officers will no longer have the power for indefinitely stopping construction work.
Additional Facts:
- Gig Worker: It is defined as a person who performs work or participates in a work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of a traditional employer-employee relationship.
- Platform workers: It is a form of employment in which organisations or individuals use an online platform to access other organisations or individuals to solve specific problems or to provide specific services in exchange for payment.
China-led mega trade bloc RCEP takes off
News: Fifteen Asia-Pacific countries led by China has signed the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
Facts:

- RCEP: It is a trade bloc comprising ASEAN countries (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand, the Philippines, Laos and Vietnam) and China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand.
- Objective: To establish a modern, comprehensive and mutually beneficial economic partnership that will facilitate the expansion of regional trade and investment and contribute to global economic growth and development.
- What does the agreement provide? The agreement allows for a common set of rules of origin to qualify for tariff reduction with other RCEP members.It also includes provisions on intellectual property, telecommunications, financial services, e-commerce and professional services.
- Major Reasons for India Pulling out of the agreement:
- Impact on Domestic industry: India was worried that RCEP could force it to cut duties on about 90% of the goods.Hence, India will be flooded with cheaper imported goods particularly from China and dairy products from Australia and New Zealand. This may have an impact on India’s domestic industry.
- Trade Deficit: India has massive trade deficits with almost all of the RCEP countries.Hence, given the export-import equation with the bloc,a free trade agreement with the grouping would have increased the trade deficit further.
- Services sector: India had demanded that the RCEP participating countries should open up their services sector so that Indian professionals and workers can have easier entry into their market.However, the countries are very sensitive about protecting this sector and have not offered much liberalisation.
- Auto-trigger mechanism: India had also asked for an auto-trigger mechanism to be institutionalised in the pact.This would serve as a kind of protective mechanism that a member country can invoke to safeguard in case of an unexpected flow of imports after RCEP comes into effect.
Explained: What is Ariel Space Mission?
News: The European Space Agency (ESA) has formally adopted Ariel, the explorer that will study the nature, formation and evolution of exoplanets.
Facts:
- Atmospheric Remote-sensing Infrared Exoplanet Large-survey (ARIEL): It is a space telescope planned for launch in 2029 by the European Space Agency.
- Objective: To observe at least 1,000 known exoplanets using the transit method, studying and characterising the planets’ chemical composition and thermal structures.
Additional Facts:
- Exoplanets: Planets that lie outside of the Solar System and orbit around stars other than the Sun are called exoplanets or extrasolar planets.
- Why do scientists study exoplanets? The search for exoplanets is driven by the possibility that life may exist beyond Earth and even if there is no evidence for this, scientists believe that their hunt for an answer will reveal details about where humans came from and where we’re headed.
Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile system(QRSAM)
News: Defence Research and Development Organisation(DRDO) has successfully test-fired Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile system(QRSAM).
Facts:
- QRSAM: It is a short range surface-to-air missile(SAM) system, primarily designed and developed by DRDO.
- Purpose: To provide a protective shield to moving armoured columns of the Army from enemy aerial attacks.
- Features: The Missile is based on a canister-based system which means that it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments.In the canister, the inside environment is controlled, thus along with making its transport and storage easier, the shelf life of weapons also improves significantly.
- Range: It has a range of around 25 to 30 km.
WHO to setup traditional medicine centre in India
News: The World Health Organisation(WHO) has announced that it will set up a Global Centre for Traditional Medicine in India.
Facts:
- Global Centre for Traditional Medicine: It seeks to support WHO’s traditional medicine strategy(2014-23) which aims to support nations in developing policies & action plans to strengthen the role of traditional medicine as part of their journey to universal health coverage.
Additional Facts:
- COVID-19 Technology Access Pool (C-TAP) initiative: It was launched by WHO with the aim to make vaccines, tests, treatments and other health technologies to fight COVID-19 accessible to all.
- Access to COVID-19 Tools(ACT) Accelerator: It is a Global Collaboration led by WHO to speed up the development, production of COVID-19 diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines and ensure equal access to treatments for rich and poor.
Govt To Provide Rs 900 Crore For Mission Covid Suraksha
News: Government of India has decided to provide Rs 900 crore to the Mission Covid Suraksha.
Facts:
- Mission Covid Suraksha: It is Department of Biotechnology initiative for research and development(R&D) of the Indian Covid vaccine.
- Purpose: The fund would only cater to R&D activity and would not cover the cost of vaccine or logistics required for its development.
China chairs second multilateral meet with South Asian partners
News: China held a virtual conference with South Asian partners amid Covid-19 pandemic.
Facts:
- Which countries participated in the conference? China, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal and Pakistan.They have called themselves as “Five Parties”.
- Objective: To discuss a collective response to the second wave of COVID-19.
- Significance: This virtual conference comes less than four months after China chaired a quadrilateral meet with the Foreign Ministers of Afghanistan, Nepal and Pakistan.Hence, this shows China’s growing engagement in the region in the wake of pandemic.