Explained: What is the Great conjunction of Saturn and Jupiter?
News: After nearly 400 years, Saturn and Jupiter will be brought closest in the night sky by an astronomical event called the “great conjunction” and popularly referred to as the “Christmas Star”.
Facts:
- Conjunction: It is the name given to any event where planets or asteroids appear to be very close together in the sky when viewed from the Earth.
- Great Conjunction: Astronomers use the term great conjunction to describe meetings of the two biggest worlds in the solar system, Jupiter and Saturn.
- The Great Conjunction happens once in about 20 years because of the time each of the planets take to orbit around the Sun.
- Time taken to orbit around the sun: Jupiter takes roughly 12 years to complete one lap around the Sun and Saturn takes 30 years (Saturn has a larger orbit and moves more slowly because it is not as strongly influenced by the Sun’s gravitational force as planets that are closer to the Sun).
Additional Facts:
- Jupiter: It is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System.Jupiter’s iconic Great Red Spot is a giant storm bigger than Earth that has raged for hundreds of years.
- Saturn: It is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the solar system.Adorned with thousands of beautiful ringlets, Saturn is unique among the planets.
Transport Ministry invites comments for introducing adoption of E20 fuel
News: Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has published a notification seeking comments from the public for adoption of E20 fuel to promote green fuel like ethanol.
Facts:
- E20 Fuel: It means blending 20% of ethanol with gasoline as an automotive fuel.
- Significance: The blending will help in reducing emissions of carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons and will also help in reducing the oil import bill, thereby saving foreign exchange and boosting energy security.
Additional Facts:
- Ethanol: Ethanol having chemical formula of C2H5OH can be produced from crops like sugarcane, maize, wheat which have high starch content. In India, ethanol is mainly produced from sugarcane molasses by the fermentation process,Hence, since ethanol is produced from plants that harness the power of the sun, ethanol is also considered as green fuel.
Explained: A look at how Parliament sessions are convened?
News: Government has decided to cancel the Winter session of Parliament, citing fears over a surge in cases due to covid-19 pandemic.
Facts:
- Constitution on Summoning of Parliament: The summoning of Parliament is specified in Article 85 of the Constitution.Like many other articles, it is based on the provision of Government of India Act,1935.
- Power to convene Session: The power to convene a session of Parliament rests with the Government.The decision is taken by the Cabinet Committee on Parliamentary Affairs which is formalised by the President, in whose name MPs are summoned to meet for a session.
- Parliamentary Calendar: India does not have a fixed parliamentary calendar.By convention (i.e. not provided by the Constitution), Parliament meets for three sessions in a year.
- The longest, Budget Session(1st session) starts towards the end of January and concludes by the end of April or first week of May. The session has a recess so that Parliamentary Committees can discuss the budgetary proposals.
- The second session is the three-week Monsoon Session, which usually begins in July and finishes in August.
- Winter Session(3rd session) is held from November to December.
Additional Facts:
Terms associated with Sessions of Parliament:
- Adjournment: Termination of the sitting of the House which meets again at the time appointed for the next sitting.
- Adjournment sine die – Termination of a sitting of the House without any definite date being fixed for the next sitting.
- Prorogation: It means the termination of a Session of the House by an order made by the President under article 85(2)(a) of the Constitution. The Prorogation of the House may take place any time even while the House is sitting.However, prorogation usually follows the adjournment of the sitting of the House sine die.
- Dissolution: It means the end of the life of the Lok Sabha either by an order made by the President under article 85 (2) (b) of the Constitution or on the expiration of the period of five years from the date appointed for its first meeting.Dissolution puts an end to the representative character of the individuals who at the time compose the Lok Sabha.
Asia-Pacific Broadcast Union(ABU)
News: Prasar Bharati CEO Shashi Sekhar Vempati has been elected as Vice President of Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union(ABU).
Facts:
- ABU: It was established in 1964 as a non-profit, non-governmental, non- political, professional association with a mandate to assist the development of broadcasting in the region.
- Objective: To promote the collective interests of television and radio broadcasters as well as key industry players and facilitate regional and international media co-operation.
- Headquarters: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Pratas Islands: A New Flashpoint in the South China Sea
News: Experts have warned about a possible Chinese attack to capture Pratas Island in the South China Sea.
Facts:
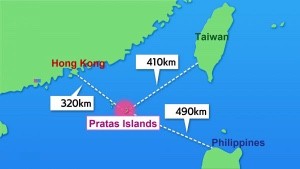
- Pratas Islands also known as Dongsha Island are located in the northern part of the South China Sea under the jurisdiction of the Republic of China (Taiwan), closer to China’s mainland coast than to the island of Taiwan.
Indian Railways issues draft National Rail Plan
News: Indian Railways has issued a Draft National Rail Plan.The plan will be a common platform for all future infrastructural, business and financial planning of the Railways.
Facts:
Key objectives of the Plan:
- Create Demand: To create capacity ahead of demand by 2030, which in turn would cater to growth in demand right up to 2050 and also increase the modal share of Railways from 27% currently to 45% in freight by 2030 as part of a national commitment to reduce net zero carbon emission by 2030.
- Forecast growth of traffic in both freight and passenger year on year up to 2030 and on a decadal basis up to 2050.
- Formulate strategies based on both operational capacities and commercial policy initiatives to increase modal share of the Railways in freight to 45% by 2030.
- Reduce transit time of freight substantially by increasing average speed of freight trains from present 22 Kmph to 50 Kmph.
- Reduce overall cost of Rail transportation by nearly 30% and pass on the benefits to the customers.
- Map the growth in demand on the Indian Railway route map and simulate the capacity behaviour of the network in future.
- Identify infrastructural bottlenecks that would arise in future with growth in demand.Select projects along with appropriate technology in both track work, signalling and rolling stock to mitigate these bottlenecks well in advance.