Govt approves inclusion of four indigenous sports in Khelo India Youth Games 2021
News: Sports Ministry has approved the inclusion of four indigenous Games to be a part of Khelo India Youth Games 2021.The games include Gatka, Kalaripayattu, Thang-Ta and Mallakhamba.
Facts:
- Gatka: It is a traditional martial art form originated from Punjab.It is associated with the Nihang Sikh Warriors and is used both as self-defense as well as a sport.
- Kalaripayattu also known as Kalari is an Indian martial art that originated in Kerala.It is believed to be the oldest surviving martial art in India.
- Thang-Ta also known as Huyen Lallong is a martial art form of Manipur and has been practised by the Meiteis.It is dedicated to fighting skill and worship.
- Mallakhamba: It is a traditional sport from Indian subcontinent and has been well-known in Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.It involves gymnasts performing aerial yoga or gymnastic postures and wrestling grips in concert with a vertical stationary or hanging wooden pole, cane, or rope.
What is Khelo India?
- Khelo India Programme was introduced by the Ministry of Sports and Youth affairs to revive sports culture in India at grass-root level.
- The objective of the programme is to build a strong framework for all sports played in our country and establish India as a great sporting nation.
- The programme is the merger of following schemes
- (a)Rajiv Gandhi Khel Abhiyan(RGKA)
- (b)Urban Sports Infrastructure Scheme (USIS)
- (c)National Sports Talent Search Scheme (NSTSS).
- Under the programme,talented players are identified in priority sports disciplines at various levels by High-Powered Committed and each will be provided annual financial assistance of Rs. 5 lakh for 8 years.
- Under this scheme,State wise budget allocation is not made and projects are sanctioned based on their viability. Funds are released project wise.
- Further,Khelo India School Games are also conducted as a part of the Khelo India programme.
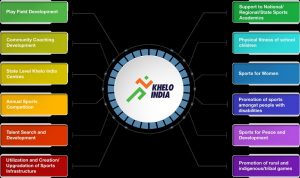
Components of the programme:To accomplish the above objectives, Khelo India programme has been divided into 12 verticals,namely:
What is Shigella Infection reported in Kerala?
News: North Kerala has been put on high alert after an 11-year-old boy died and 20 suspected cases of shigella bacterial infection were reported.
Facts:
- Shigella Infection (shigellosis) is an intestinal infection caused by a family of bacteria known as shigella.
- Transmission: Contaminated food, water are the source of the infection. The bacteria spreads not only through surfaces — touching an infected surface and then touching the mouth — but also from eating food prepared by someone carrying the infection.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include diarrhoea, fever, stomach cramps which can last for seven days.
- Treatment: It is generally done through antibiotics which can shorten the duration of the illness.
- Susceptible Group: Children under age 10 are most likely to get shigella infection but it can occur at any age.
- Precautions: Doctors advise frequently washing hands with soap and running water to avoid infections such as Shigella.
Defence Minister hands over DRDO systems to Armed Forces Chiefs
News: Defence Minister has handed over three indigenously developed Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) systems to Army, Navy and Air Force.
Facts:
What are the three indigenously developed systems?
- Indian Maritime Situational Awareness System (IMSAS): It is a state-of-the-art and high performance intelligent software system that provides Global Maritime Situational Picture, marine planning tools and analytical capabilities to Indian Navy.
- Developed by: Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (CAIR), Bengaluru and Indian Navy has jointly conceptualised and developed the product and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Bengaluru has implemented it.
- ASTRA
- Astra is the indigenously developed Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM).
- The BVRAAM technology enables fighter-pilots to shoot precisely at the enemy targets which are beyond their visual range.
- The missile has been developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The missile has a range of over 70 km.It can fly towards the target at a speed of over 5,555 km per hour.
- The missile has a 15-kilogramme high-explosive pre-fragmented warhead and the missile is also capable of engaging targets of different ranges and altitudes.
- Further,Astra missile also has some highly advanced features like Electronic Counter-Countermeasures or ECCM.This feature enables Astra missile to overcome defensive measures put forth for the target by the enemy.
- The ASTRA Mk-I Weapon System integrated with SU-30 Mk-I aircraft is being inducted into the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- Border Surveillance System(BOSS): It is an all-weather electronic surveillance system successfully designed and developed by Instruments Research and Development Establishment (IRDE), Dehradun.
- Purpose: The system has been deployed at Ladakh border area for day and night surveillance and facilitates monitoring and surveillance by automatically detecting the intrusions in harsh high-altitude sub-zero temperature areas with remote operation capability.
North Eastern Region Power System Improvement Project
News: Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved the Revised Cost Estimate (RCE) for the North Eastern Region Power System Improvement Project (NERPSIP).
Facts:
- NERPSIP Scheme: The Scheme was initially approved in 2014 as a Central Sector Plan Scheme of the Ministry of Power.
- Funding: The scheme is being funded with the assistance of the World Bank fund and by the Government of India through the Budget support of the Ministry of Power on a 50:50 basis.
- Objective: Government’s commitment for the total economic development of the North Eastern Region and to strengthen the Intra-State Transmission & Distribution Infrastructure in the North East Region.
- Implementation: The scheme is being implemented through Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (POWERGRID).
- Beneficiary States: Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura and is targeted to be commissioned by December 2021.
‘Any exploitation of Sentinel Island will wipe out tribals’
News: Anthropological Survey of India(AnSI) has said that any exploitation of the North Sentinel Island of the Andamans for commercial and strategic gain would spell the death knell for its occupants, the Sentinelese, a most secluded, particularly vulnerable tribal group(PVTG).
Facts:
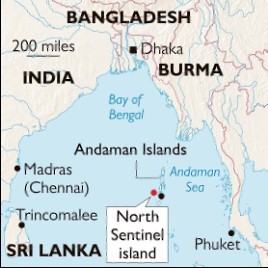
- Sentinelese also known as the Sentineli are a negrito tribe who live on the North Sentinel Island of the Andaman.
- Occupation: Sentinelese are hunter-gatherers, likely using bows and arrows to hunt and more rudimentary methods to catch local seafood.
- Language: It is known that the Sentinelese speak their own language, the Sentinelese language.
- Population: Currently,their numbers are believed to be less than 150 and as low as 40.
- How are they protected? The Govt. of India has issued the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (Protection of Aboriginal Tribes) Regulation, 1956 to declare the traditional areas occupied by the tribes as reserves and prohibited entry of all persons except those with authorisation.
Additional Facts:
- Anthropological Survey of India(AnSI): It was founded in 1945 as the apex Indian government organisation involved in anthropological studies and field data research for human and cultural aspects.It is operating under the Ministry of Culture and is headquartered in Kolkata.
- Tribes of Andaman and Nicobar: The Andaman Islands are home to four ‘Negrito’ tribes namely the Great Andamanese, Onge, Jarawa and Sentinelese.Nicobar Islands are home to two ‘Mongoloid’ tribes – the Shompen and Nicobarese.
US FDA Approves Intentional Genomic Alteration in Line of Domestic Pigs
News: US Food and Drug Administration(FDA) has approved a first-of-its-kind intentional genomic alteration(IGA) in a line of domestic pigs referred to as GalSafe pigs.These pigs may be used for food and human therapeutics.
Facts:
- What is intentional genomic alteration in animals? It means making specific changes to the genome of the organism using modern molecular technologies that are popularly referred to as “genome editing” or “genetic engineering”.
- Purpose: Such changes in the DNA sequence of an animal may be carried out for research purposes to produce healthier meat for human consumption and to study disease resistance in animals among other reasons.
- Difference: The FDA maintains that the only difference between an animal with an IGA and one that does not have an IGA is that the IGA gives them a new trait or characteristic such as faster growth or resistance to certain diseases.
Additional Facts:
- Genome editing: It is a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism.Editing DNA can lead to changes in physical traits like eye color and disease risk.
India looks at integrating more countries into coastal radar network
News: India is in talks with Maldives, Myanmar and Bangladesh to set up coastal radar stations as part of efforts to further expand the coastal radar chain network meant to enable real-time monitoring of the high seas for threats.
Facts:
- Countries already integrated in the Coastal Radar Network: Mauritius, Seychelles and Sri Lanka have been integrated into the country’s coastal radar chain network.
Other Developments:
- Information Management and Analysis Centre(IMAC): It was established in 2014 and is the nodal centre for maritime security information collation and dissemination.
- Location: Gurgaon, Haryana
- Operated by: It is jointly operated by the Navy and Coast Guard.
- White Shipping agreements: It refers to exchange of relevant advance information on the identity and movement of commercial non-military merchant vessels.
- Indian Navy has been authorised to conclude white shipping agreements with 36 countries and three multilateral constructs. So far agreements have been concluded with 22 countries and one multilateral construct.
- Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean region(IFC-IOR): It was set up in 2018 within the premises of the IMAC to coordinate with regional countries on maritime safety and security and act as a regional repository of maritime data.
Explained: What is Positive Pay Mechanism?
News: From January 1, 2021, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will introduce the ‘Positive Pay System’ for cheque transactions above Rs 50,000 in a bid to enhance safety and eliminate frauds.
Facts:
- Positive Pay Mechanism: It involves a process of reconfirming key details of large-value cheques.
- Process: Under this, the issuer of the cheque submits electronically through channels like SMS, mobile app and Internet banking, certain minimum details of cheque to the drawee bank, details of which are cross-checked with the presented cheque by Cheque Truncation System(CTS).Any discrepancy is flagged by CTS to the drawee bank and presenting bank who then take redressal measures.
- Cheque Limits: Banks will enable the new system for all account holders issuing cheques for amounts of Rs 50,000 and above.It is mandatory in case of cheques for amounts of Rs 5,00,000 and above.
- Developed by: National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) will develop the facility of Positive Pay in CTS and make it available to participant banks.