Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020
News: Union Government has for the first time laid down Rights to the Electricity Consumers through “Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020”.
Facts:
- The Ministry of Power framed the proposed rules under Section 176 of the Electricity Act 2003.
- Objective: To empower consumers with rights that would allow them to access continuous supply of quality, reliable electricity.
- Note: Electricity is a concurrent subject and the Centre has the power to make rules to be implemented in each state.
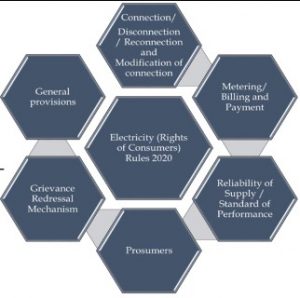
Key Provisions of the Rules:
Source: eqmagpro.com
- Rights and Obligations:
- Distributor: It is the duty of every distribution licensee to supply electricity on request made by an owner or occupier of any premises in line with the provisions of Act.
- Consumer: Whereas, consumers have a right to have minimum standards of service for supply of electricity from the distribution licensee.
- Release of new connection and modification in existing connection: Maximum time period of 7 days in metro cities and 15 days in other municipal areas and 30 days in rural areas, has been fixed to provide new connection and modify an existing connection.
- Metering: No connection shall be given without a meter that shall be a smart prepayment meter or prepayment meter.
- Billing and Payment: There should be transparency applicable consumer tariff and bills, with the option to pay advance bills.
- Reliability of supply: The distribution licensee shall supply 24×7 power to all consumers. However, the Commission may specify lower hours of supply for some categories of consumers like agriculture.
- Consumer as prosumer: While the prosumers will maintain consumer status and have the same rights as the general consumer, they will also have the right to set up Renewable Energy (RE) generation units including roof top solar photovoltaic (PV) systems – either by himself or through a service provider.
- Prosumer: It means a person who consumes electricity from the grid and can also inject electricity into the grid for distribution licensees using the same point of supply.
- Compensation mechanism: Automatic compensation shall be paid to consumers for which parameters on standards of performance can be monitored remotely.
- Call Centre for Consumer Services: Distribution licensee shall establish a centralized 24×7 toll-free call center.
- Grievance redressal mechanism: Consumer Grievance Redressal Forum (CGRF) to include consumer and prosumer representatives. Though Maximum timeline of 45 days has been specified for grievance redressal, licensee shall specify the time within which various types of grievances will be resolved.
‘Firefly bird diverters’ to save the Great Indian Bustard
News: Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change(MoEFCC) along with Wildlife Conservation Society(WCS) has come up with a unique initiative — a “firefly bird diverter” for overhead power lines in areas where Great Indian Bustard (GIB) populations are found in the wild.
Facts:
- Firefly bird diverters: These are flaps installed on power lines, a reason for many death among GIB. They work as reflectors for bird species like the GIB. Birds can spot them from a distance of about 50 meters and change their path of flight to avoid collision with power lines.
Great Indian Bustard:
- It is one of the heaviest flying birds (weighing up to 15kgs).They inhabits dry grasslands and scrublands on the Indian subcontinent
- Habitat: It is endemic to the Indian subcontinent. It is found in Rajasthan (Desert National park), Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh in India and parts of Pakistan.
- IUCN Red List: It is a critically Endangered species with less than 150 birds left in the wild.
- Indian Wildlife (Protection)Act,1972: Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix I
- Threats:
- Death by collision with infrastructure, particularly power lines and wind turbines,
- Depletion of grasslands,
- hunting,
- development of mines and human habitation in and around their habitats among others.
- Conservation Initiatives:
- Project Great Indian Bustard: It was launched by Rajasthan Government with the objective of conservation of the remaining population of critically endangered Great Indian Bustard(Ardeotis nigriceps) locally called Godawan.
Additional Facts:
- IUCN Species Survival Commission(SSC): It is a science-based network of more than 9,000 volunteer experts from almost every country of the world, all working together towards achieving the vision of, “A just world that values and conserves nature through positive action to reduce the loss of diversity of life on earth”.
US President Presents PM Modi With Top US Honour ‘Legion Of Merit’
News: US President has presented the prestigious Legion of Merit to Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
Prime Minister received this award for his initiatives in elevating the U.S.-India strategic partnership.
- Along with Prime Minister, the award was also presented to Former Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison.
Facts:
- Legion of Merit Award: It is a military award of the United States Armed Forces given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in performance of outstanding services and achievements.
- It is awarded to members of the seven uniformed services of the United States as well as to military and political figures of foreign governments.
- The previous Indian recipients of the award include Field Marshal KM Cariappa (1950) and Satyawant Mallana Srinagesh (1955).
Western Ghats home to 3,387 leopards
News: According to Status of Leopards in India 2018 report, released by Minstry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Western Ghats region is home to 3,387 leopards stealthily roaming around its forests.
As for region-wide distribution is concerned, the highest number of 8,071 leopards were found in central India and Eastern Ghats. The highest concentration of the leopard in India is estimated to be in Madhya Pradesh (3,421) followed by Karnataka (1,783) and Maharashtra (1,690).
Leopards in Western Ghats:
- Karnataka tops the list in Western Ghats region with 1,783 leopards, followed by Tamil Nadu (868), Kerala (650) and Goa (86).
- Leopard population of the Western Ghats landscape was reported from the four distinct blocks.
- Northern Block: The Northern block covered the forests of Radhanagari and Goa covering Haliyal- Kali Tiger Reserve, Karwar, Honnavar, Madikeri, Kudremukh, Shettihalli WildLife Sanctuary(WLS), Bhadra and Chikmagalur.
- Central Block: The Central population covered southern Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and northern Kerala covering the forests of Virajpet, Nagarhole, Bandipur, Mudumalai, Sathyamangalam, Nilgiris, Silent Valley, Wayanad, BRT Hills, MM Hills, Cauvery WLS, Bannerghatta National Park.
- Second Central Cluster: A second central cluster covering central Kerala and Tamil Nadu comprising the Parambikulam-Anamalai – Eravikulam – Vazhachal population.
- Southern Block: The southern leopard population block in southern Kerala and Tamil Nadu comprised the forests of Periyar-Kalakad Mundanthurai -Kanyakumari.
Additional Facts:
Indian Leopard or Common Leopard:
- The Indian leopard (Panthera pardus fusca) is a leopard subspecies widely distributed on the Indian subcontinent.These are the smallest of the big cats known for its ability to adapt in a variety of habitats.
- Melanism is a common occurrence in leopards, wherein the entire skin of the animal is black in colour, including its spots.Leopards are nocturnal animals which means they hunts by night.It feeds on smaller species of herbivores found in its range, such as the chital, hog deer and wild boar.
- Vegetation: In India, the leopard is found in all forest types, from tropical rainforests to temperate deciduous and alpine coniferous forests. It is also found in dry scrubs and grasslands, the only exception being desert and the mangroves of Sundarbans.
- Distribution: Its range stretches from the Indus river in the west, the Himalayas in the north, and all the way to the lower course of the Brahmaputra in the east.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- Wildlife (Protection)Act,1972: Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix I
- Concerns:
- Fragmentation of forests as well as the quality of forests
- Human-Leopard conflict: Leopards are not like tigers who don’t like humans and therefore don’t venture out. Leopards are far more adaptable and when loss of habitat takes place, they move closer to human settlements and that’s when the conflict takes place.
- Poaching of Leopards
- Depletion of natural preyamong others.
Air Quality Commission directs for 100% switching over of industries in Delhi to PNG
News: The Commission for Air Quality Management in NCR and Adjoining Areas reviewed the progress of switching over of Industries operating in Delhi to Piped Natural Gas with the Government of NCT of Delhi, GAIL and Indraprastha Gas Limited.
Facts:
- Commission for Air Quality Management in NCR and Adjoining Areas: The commission is a statutory authority setup to tackle air pollution and to monitor and improve air quality in the National Capital Region(NCR) and adjoining areas.
- Composition:
- Chairperson: The Commission is headed by a full-time chairperson who has been a Secretary to the Government of India or a Chief Secretary to a State government.The chairperson will hold the post for three years or until s/he attains the age of 70 years.
- Members: It has members from several Ministries as well as representatives from the stakeholder States.It will also have experts from the CPCB, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Civil Society.
- Powers:
- The Commission has been conferred with the power to lay down air quality parameters, discharge of environmental pollutants parameters, to inspect premises violating the law, order closure of non-abiding industries or plants among others.
- The commission can supersede all existing bodies such as the CPCB and even the state governments of Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh. It will have the powers to issue directions to the states.
- Orders of the Commission shall prevail in case there is a conflict between the Central Pollution Control Board and the State Pollution Control Boards.
- It will have powers to restrict the setting up of industries in vulnerable areas and will be able to conduct site inspections of industrial units.
- Penalties and Offences
- Non-compliance of orders of Commission: The commission can impose a penalty of imprisonment for terms that may extend to 5 years or fine extending upto INR 1 Crore or with both for non-compliance.
- Offence committed by Company- For offence committed by any Company, every person who at the time of offence was directly in charge for or responsible for the conduct of the business of the company, will be held guilty for offence.
- Appeal: Any appeal from the Order of the Commission would lie before the National Green Tribunal (NGT).
World Bank Signs $500 Million Project to Develop Green, Resilient and Safe Highways in India
News: The Government of India and the World Bank has signed a $500 million Green National Highways Corridors Project.
Facts:
- Objective: To demonstrate safe and green National Highway corridors in selected States and enhance the institutional capacity of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways in mainstreaming safety and green technologies.
- States covered under the project: Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
- Key Features of the project:
- The project supports an in-depth analysis of gender-related issues in the transport sector along with help in creating jobs for women by training women-led micro enterprises and women collectives to implement green technologies in the highway corridors.
- The project will also strengthen and widen existing structures; construct new pavements, drainage facilities and bypasses; improve junctions and introduce road safety features.
News: Union Minister of Sports & Youth Affairs has virtually inaugurated 8 Khelo India State Centres of Excellence (KISCEs) across India.
Facts:
- Khelo India Programme: It was introduced by the Ministry of Sports and Youth affairs.
- Aim: To revive the sports culture in India at the grass-root level by building a strong framework for all sports played in our country and establish India as a great sporting nation.
- Objectives:
- Mass participation of youth in annual sports competitions through a structured competition;
- Identification of talent
- Guidance and nurturing of the talent through existing sports academies and new set up either by the central Government or State Government or in PPP mode.
- Creation of Sports Infrastructure at mofussil, Tehsil, District, State levels among others.
- Merger: The scheme is a merger of three schemes namely:
- Rajiv Gandhi Khel Abhiyan: Infrastructure in rural areas and encouraging sports through competitions
- Urban Infrastructure Scheme: Development of Infrastructure in urban areas.
- National Sports Talent Search: Identifying sports talent.
- Key Features of the Scheme:
- Under the scheme, Talented players identified in priority sports disciplines at various levels by the High-Powered Committee will be provided annual financial assistance of INR 5 lakh per annum for 8 years.
- State wise budget allocation is not made and projects are sanctioned based on their viability. Funds are released project wise.
- Verticals: To meet the objectives of Khelo India, the entire programme is divided in 12 verticals as mentioned in the below picture:
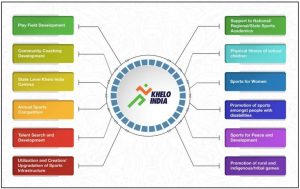
Note: Sports being a State subject, the responsibility of promotion of sports, including identification of young talent and its nurturing rests with State Governments. Government of India supplements the efforts of State Governments through its various schemes.
News: The United Nations (UN), United Kingdom (UK) and France have co-hosted the Climate Ambition Summit 2020 in partnership with Chile and Italy to mark five years since the adoption of the Paris Agreement.
Facts:
- The summit brings together leaders from across all levels of government, as well as the private sector and civil society, to present more ambitious and high-quality climate commitments, and measures to limit global warming to 1.5C.
Key Takeaways from the summit:
- The United Kingdom has pledged to double its climate finance contribution to USD 15.5 billion over the next five years.
- The European Investment Bank has announced a goal of 50% of investments going toward the climate and environment sectors by 2025. It also called for climate finance commitments to support the most vulnerable and ambitious adaptation plans and underlying policies.
- China has committed to lower its carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP by over 65% from 2005 levels by 2030.
India’s achievements:
- India has reduced emission intensity by 21% over 2005 levels.
- Solar capacity has grown from 2.63 Gigawatts in 2014 to 36 Gigawatts in 2020.
- Renewable energy capacity is the fourth largest in the world.
- It will reach 175 Gigawatts before 2022.
- India has also set a new target of 450 Gigawatts of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- On the world stage, India has pioneered two major initiatives: (1) The International Solar Alliance; (2) Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure.
Initiatives launched:
- Race To Zero: It is a global campaign launched by UNFCCC to rally leadership and support from businesses, cities, regions, investors for a healthy, resilient, zero carbon recovery that prevents future threats, creates decent jobs, and unlocks inclusive, sustainable growth.
- Net Zero Asset Managers initiative: It is a leading group of global asset managers that commit to support the goal of net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 or sooner, in line with global efforts to limit warming to 1.5°C